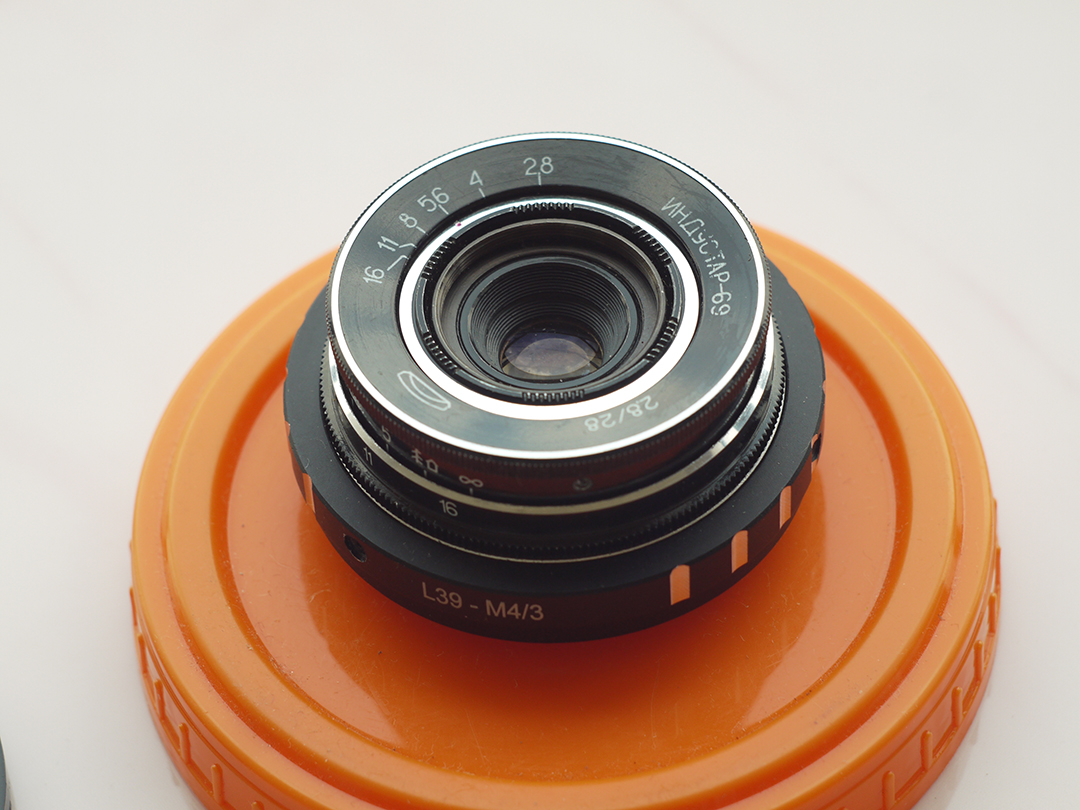
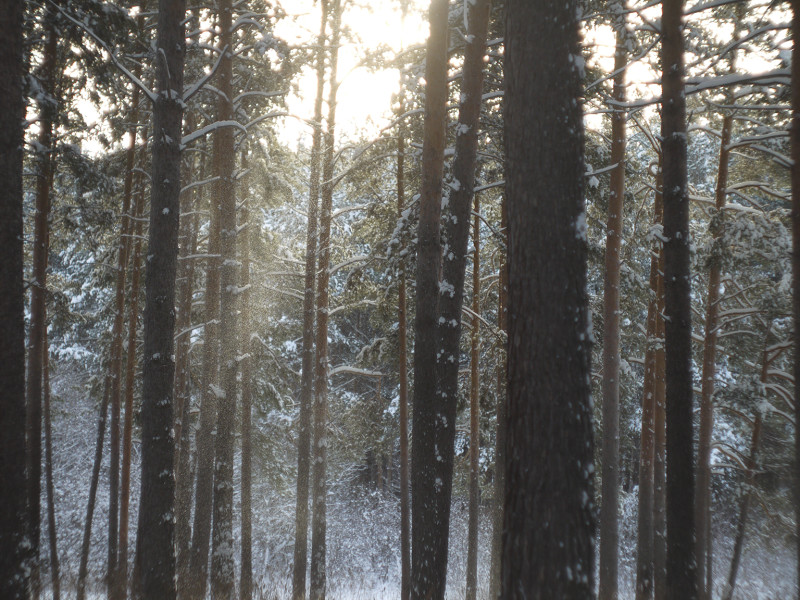
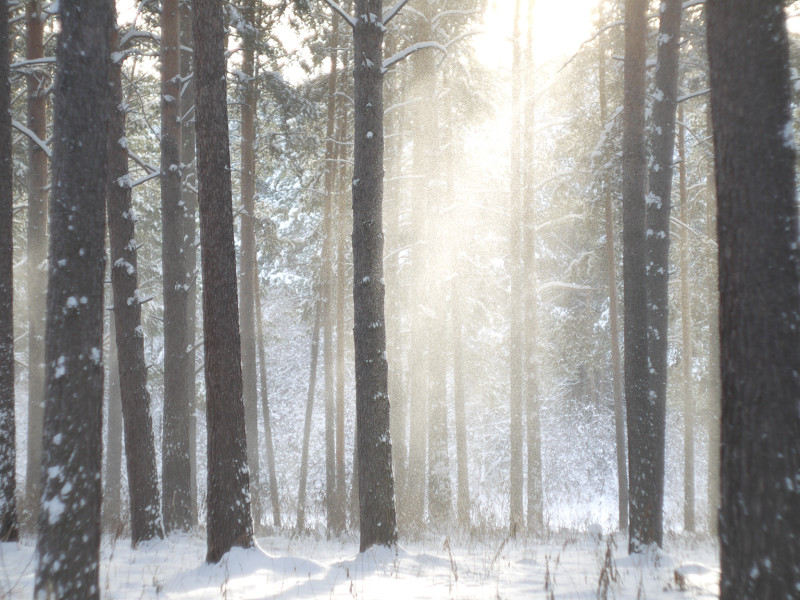
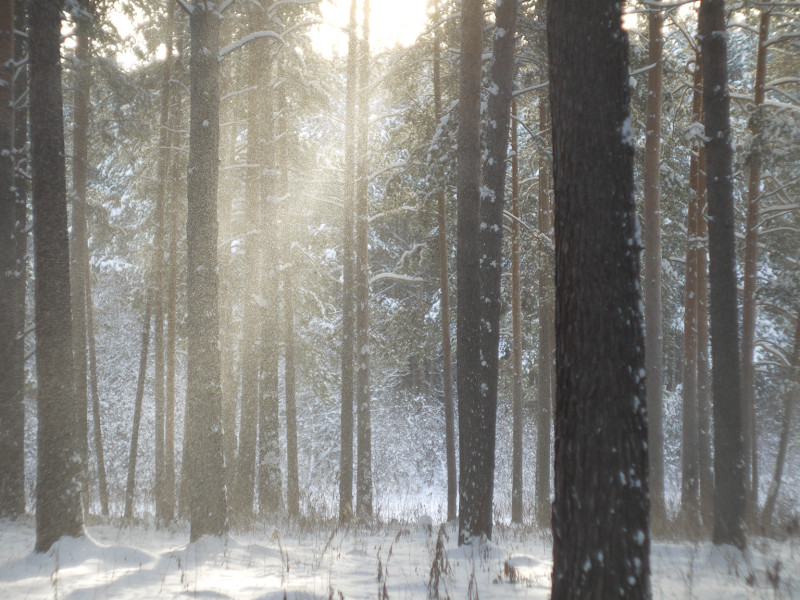
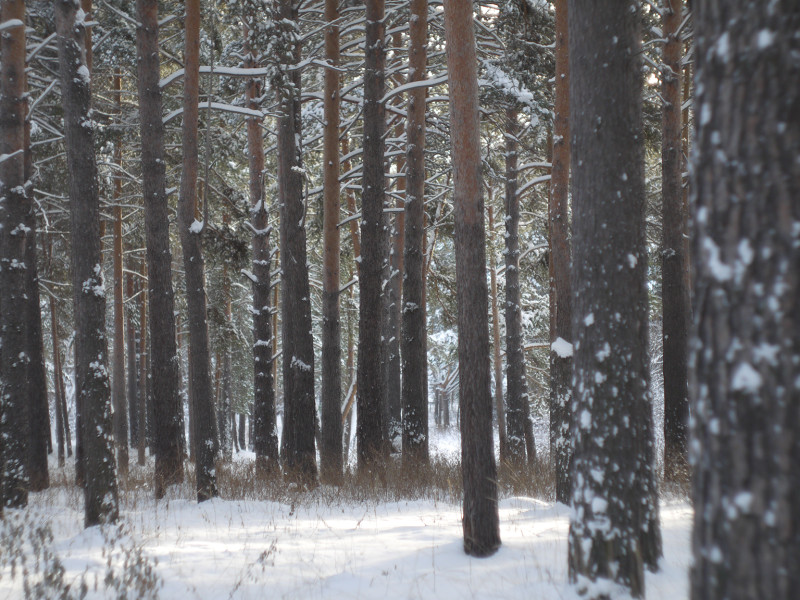
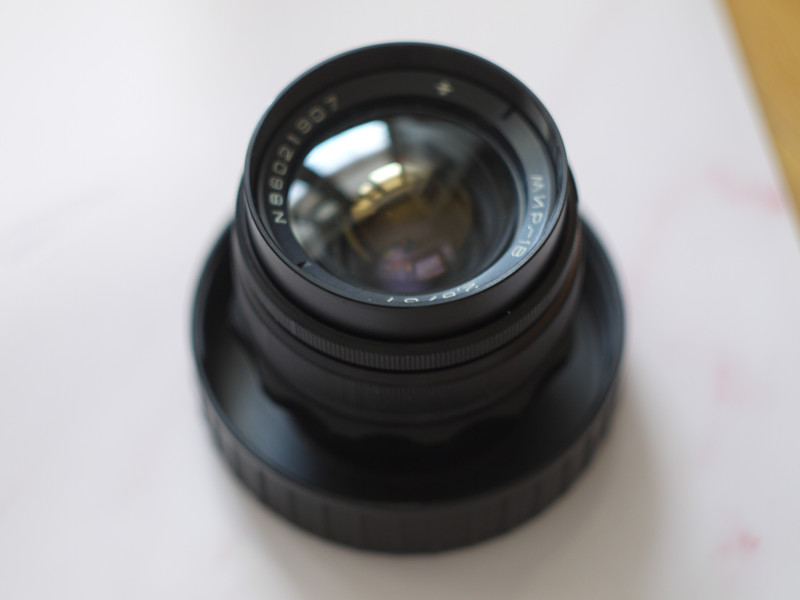
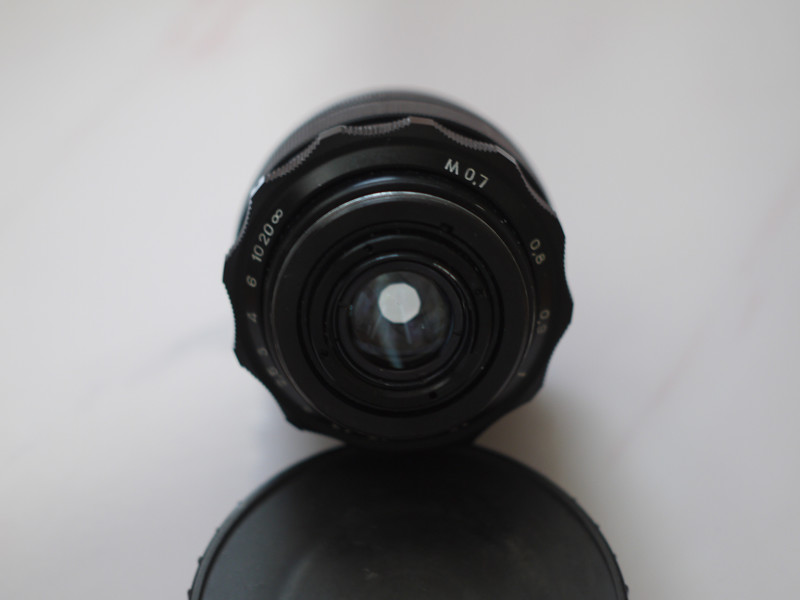
At last I have a time to test M39 photo lens Industar 69 on Micro 4/3 sensor, it is designed for frame size, which is equal to APS-C sensor; so on Micro 4/3 matrix its crop-factor is 1.3 – in this amount of times its effective focal length is increased and its angle of view is decreased. For its frame size it has following characteristics : 28 mm focal distance, f/2.8-16 diaphragm, standard minimal focusing distance is 0.65 m ( after readjustment there is ability to focus with it much closer, approximately on 10 – 20 cm distance in front of lens ) and field of view is 56 degrees ( 43.08 degrees on Micro Four Thirds matrix ). Lens has 5 diaphragm blades without blackening, 4 lens elements in 3 groups with single-layer optical anti-reflective and protective coating and 22.5 mm thread over frontal glass for optical filters. Its optical resolution is 45/20 lines on mm center/borders ( some sources tell, that it is equal to 44/22 lines on mm ) – this is close to Helios 44M-7, but below it, especially on borders.
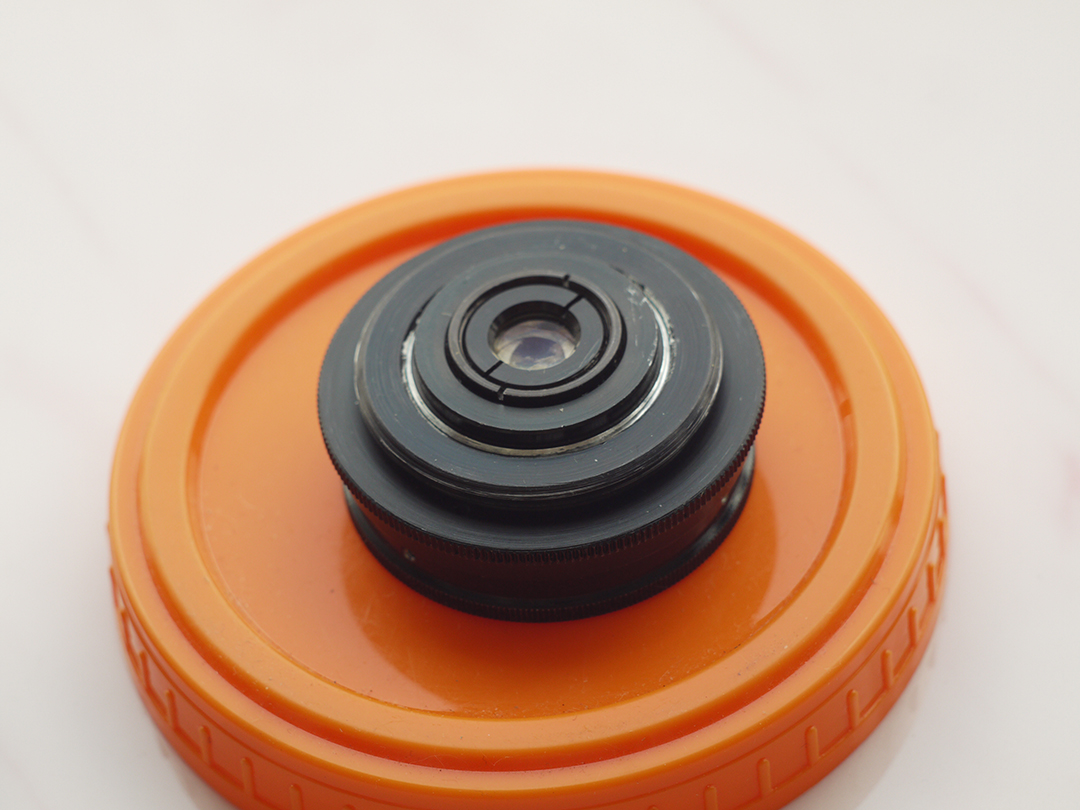

Operating segment ( distance between mount of lens to sensor/film ) of Industar 69 is equal to 27.5 mm and differs from standard 28.8 mm of M39 mount. So, to be able to focus on infinity, there is need to perform readjustment of lens. There are many ways to do this, I made it this way : unscrewed frontal body part with 3 small screws on the sides, removed stoppers, which do not allow lens elements block to rotate past defined limits. Focusing of optics is performed by movement of the whole glasses block, so there is only need to make it so, that it can be rotated to 27.5 mm inside of camera; after removing of stoppers it almost focuses on infinity and there is need to screw it slightly more. Inside around thread there is small aluminum protrusion, which can be whittled away to allow to move glasses block further. I made exactly this way with use of rasp, whittled slightly more, than needed, and when it is screwed completely, Industar 69 goes slightly farther, than infinity, there is ability to just screw it not completely to focus on far away objects.
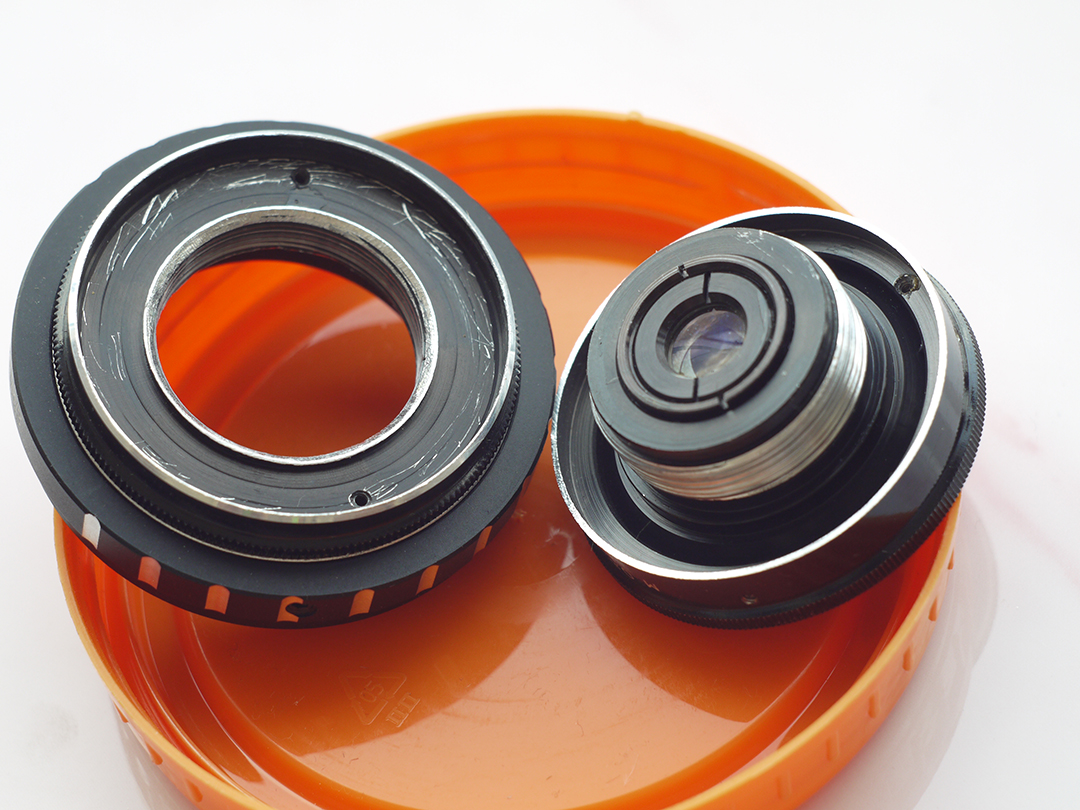

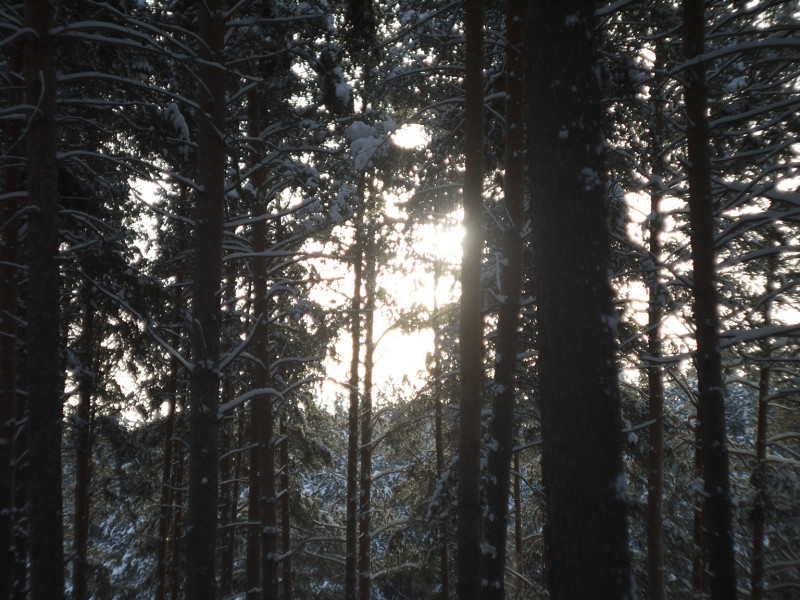
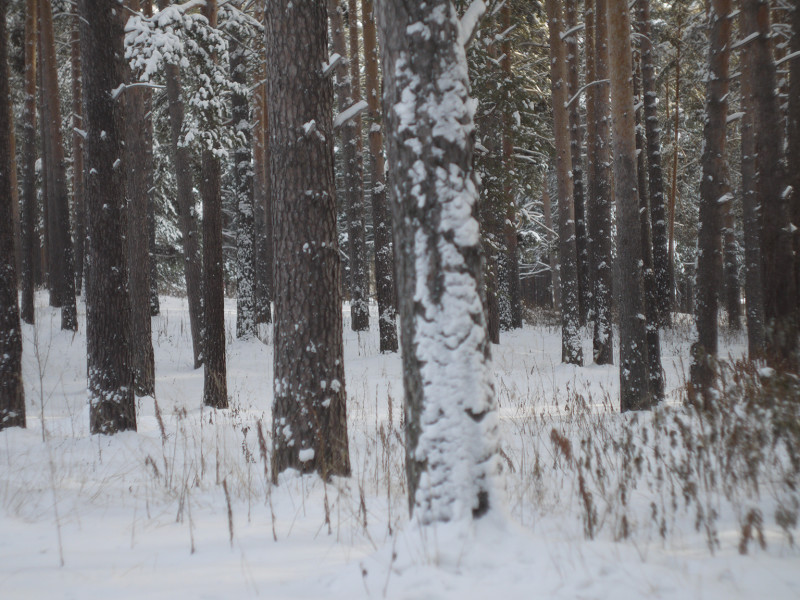
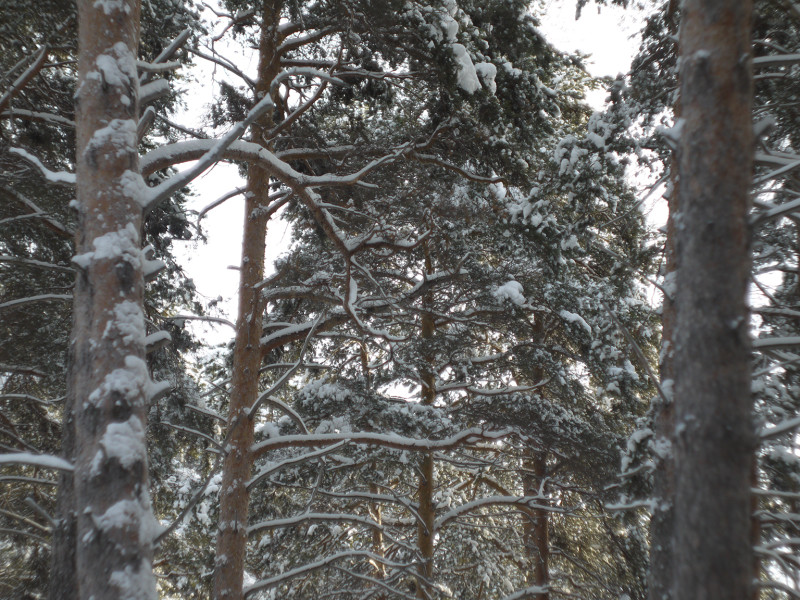
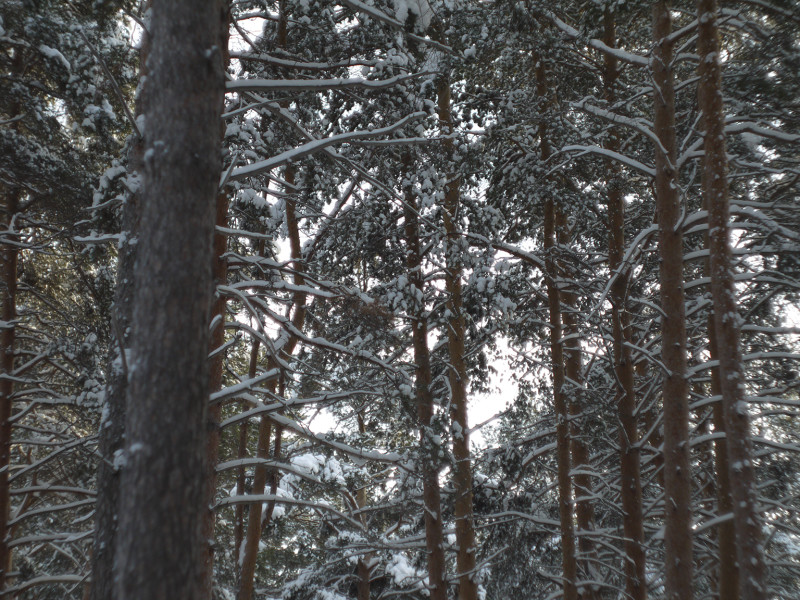
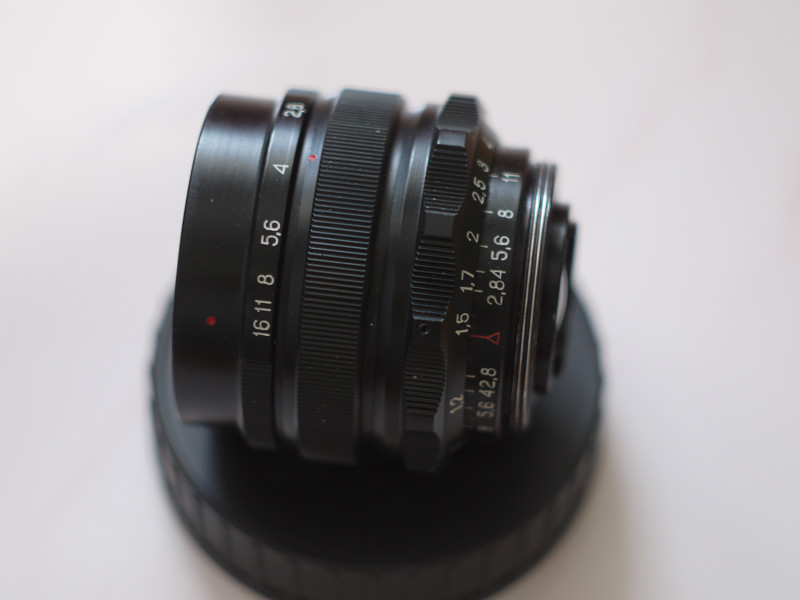
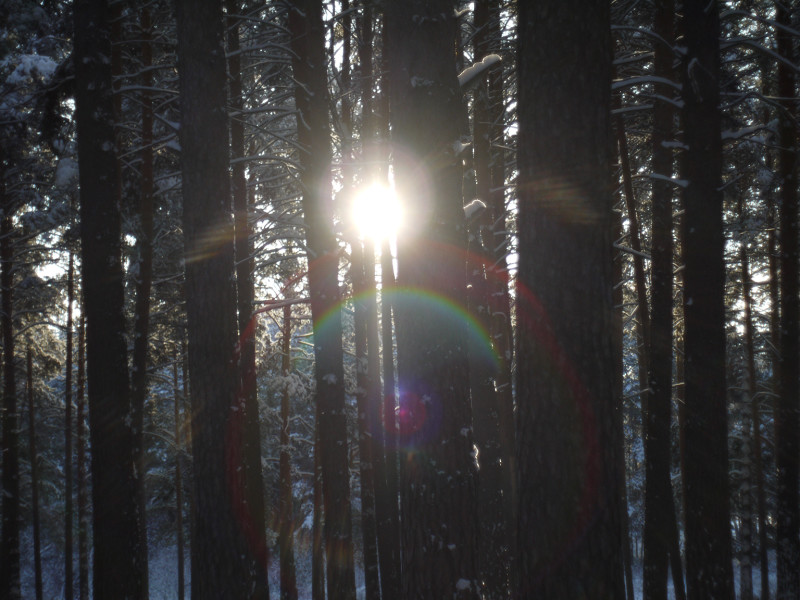
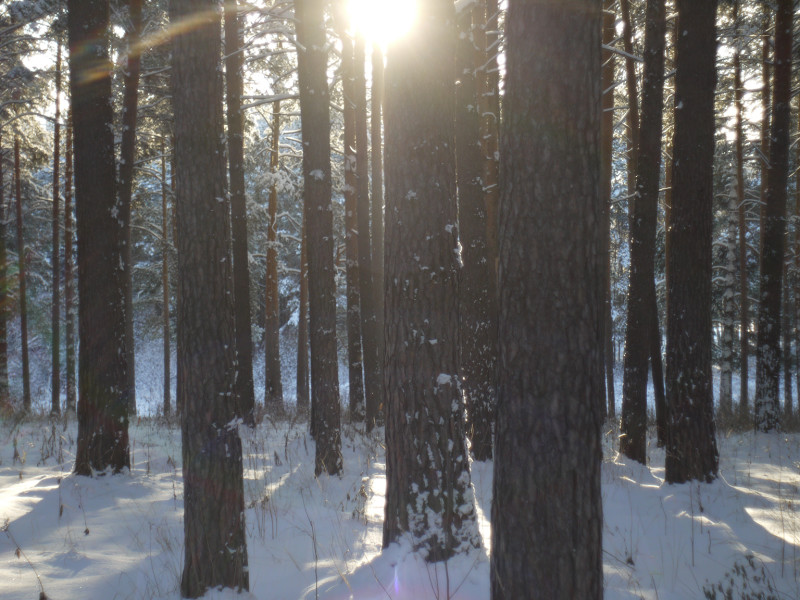
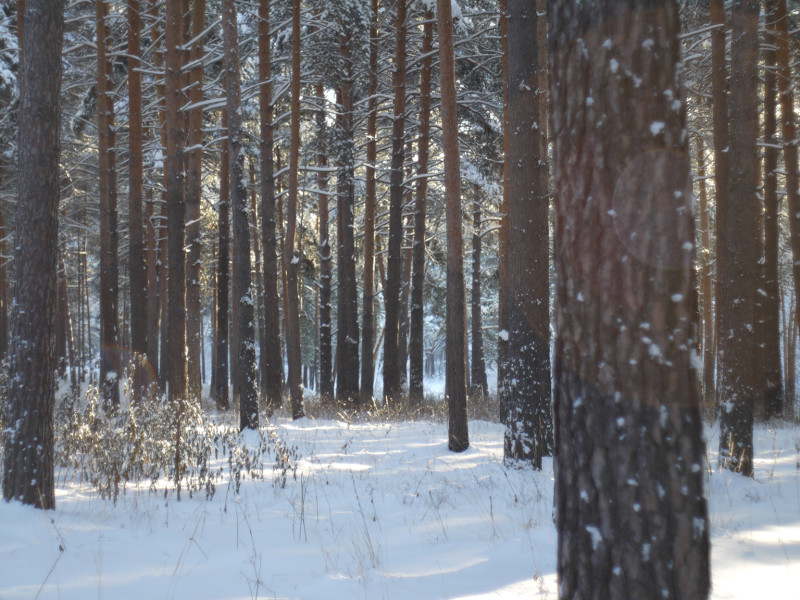
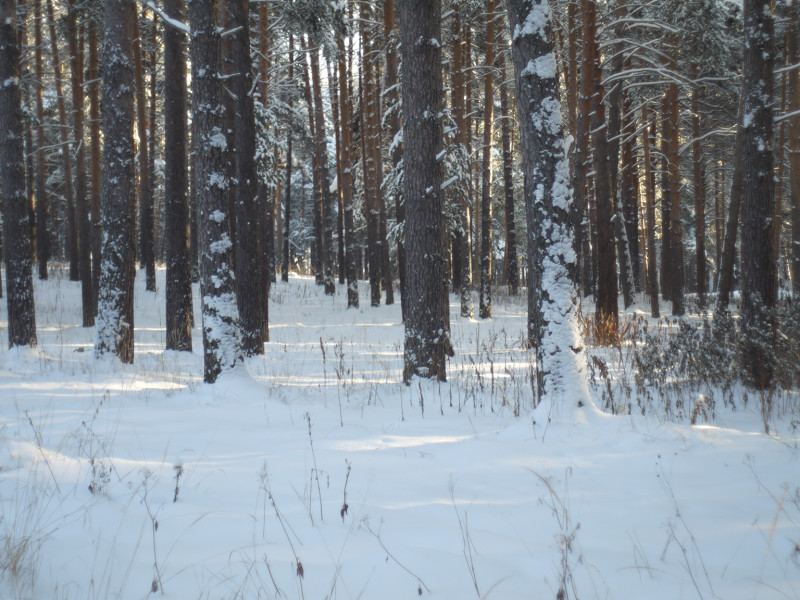
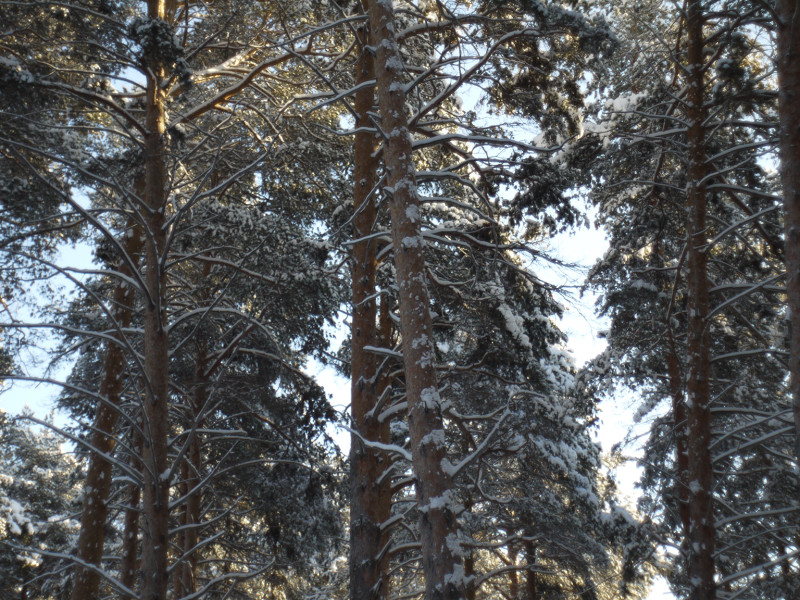
After this frontal body part of Industar 69 can be installed back, taking into account precise setting of diaphragms scale; after readjustment scale of focusing distances has not much meaning, because lenses elements block can be unscrewed much further and there is ability to focus on objects in 10 – 20 cm in front of camera for macro photographs. Additionally macro rings can be used for focusing on even closer objects. As it can be seen in test photos, Industar 69 does not have positional and magnification chromatic aberrations – this is an advantage of fixed lens with small glasses amount. All photos are made with diaphragm f/5.6, because on more open ones it blurs frame sides too much. It works good with counter and side lighting : does not loose contrast and have no large flares amount, because its frontal lens placed deeply in its body and this is again advantage of lenses with small optical elements amount. However with some angles of Sun close to frame border there is a colorful violet strip : sometimes it can be used in artistic purposes, sometimes it can disturb, but it appears only in narrow angles range and there is always ability to choose position and shooting angle to make it so, that it’ll not appear.
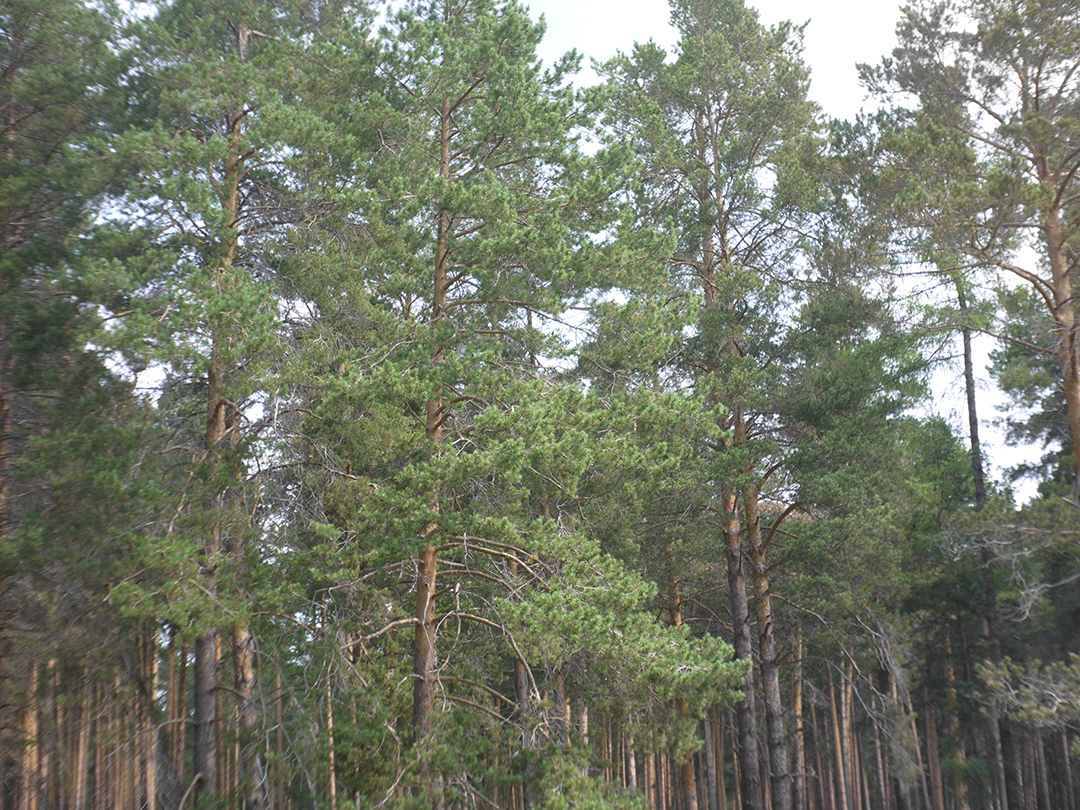

One of the advantages of Industar 69 is its small sizes and mass – in this area with adapter to camera mount from M39 it is close to modern compact lenses of mirrorless cameras. Its diaphragm control ring is located on frontal side, very thin and often rotates tightly; so, to adjust it there is need to rotate front of camera to oneself and, rotating this ring, it is easy to change lens focusing – this is its minus, but it is a payment for its compactness and small mass. When diaphragm is strongly closed its hole looks like five edges Soviet quality mark, so in blur zone light sources and bright points have the same form.
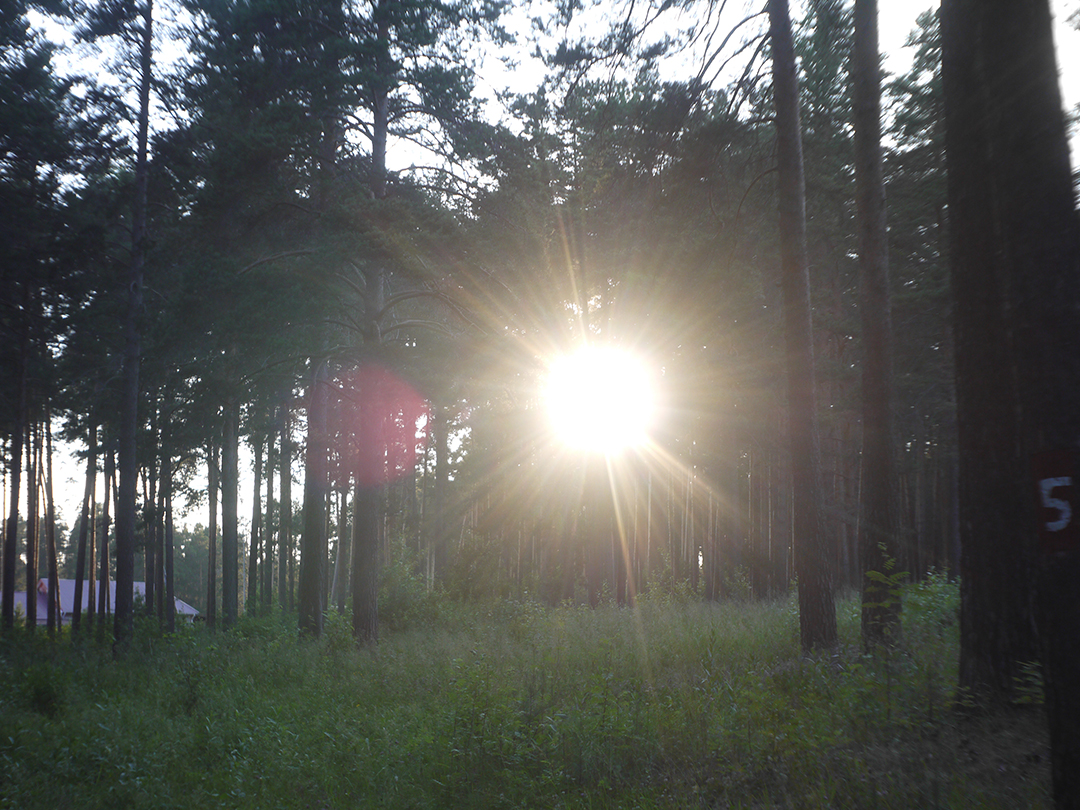

All in all there is ability to say, that lens blurs frame edges very much, even on diaphragms 5.6 – 8 – the most optimal ones for majority of lenses, sides are blurred on 20 – 30 % of radius, top and bottom on 20 % on Micro 4/3 sensor; on its constructive APS-C matrix this effect ‘ll be visible even more. Especially on open diaphragms. On many of test photos it can be clearly seen how strongly it blurs edges of frame. So, it can be used in scenes, where sharpness in whole field of view is not needed : in macro shooting, portraits making, shooting of small groups of people in center of frame and objects on the speed – here blurring of sides does not affect, slightly noticeable and even useful. However with landscapes, architecture, interior and large groups of people in whole FOV of shooting, where sharpness in whole FOV is needed, Industar 69 will give large blurring of frame edges and is not very suitable for these tasks. There is also need to note, that in macro it is quite good, however there are lenses with close price, which provide much better quality in this kind of photos making.
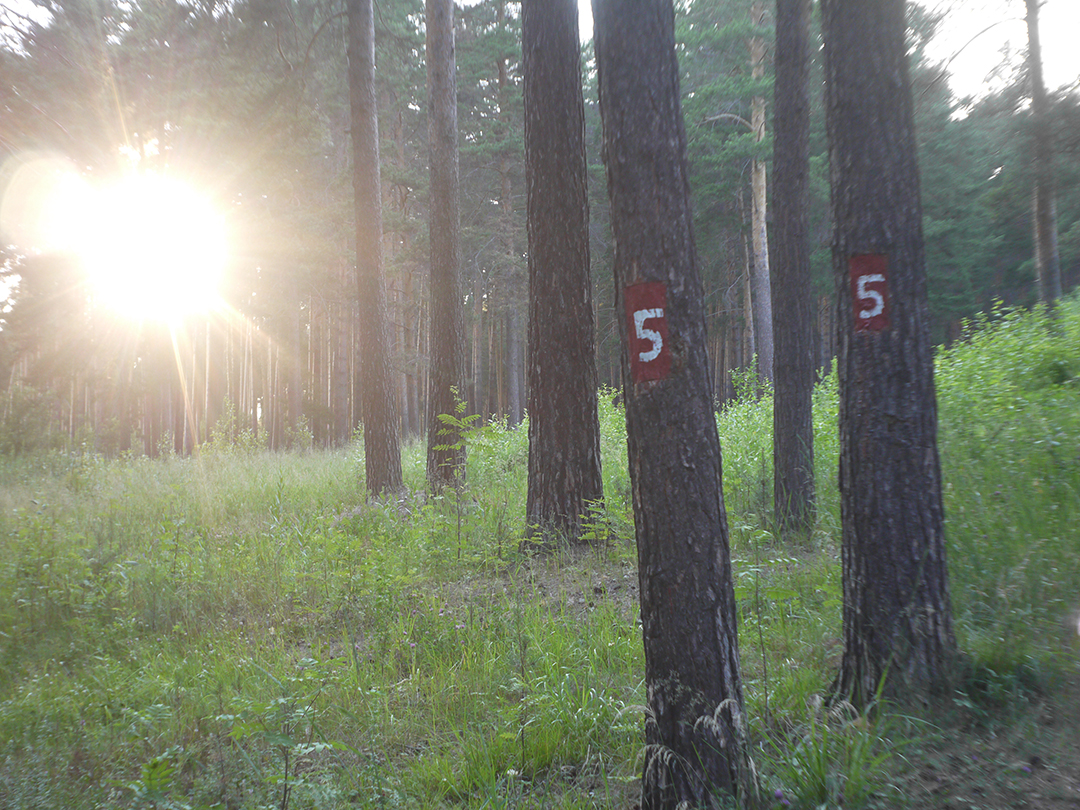

So, Industar 69 is quite specific lens for narrow set of tasks, some people ask for it around 50 USD or more, as wide angle lens for crop-matrices – it is not worth such amount of money, because 20 – 50 % of frame sides are blurred and all advantages of wide angle are blurred with them. 10 – 20 USD is optimal price for it, because it is oriented only on narrow set of tasks and there are lenses with close price, which have much better sharpness in center and sides of frame. In 1 – 2 weeks I’ll make photos of test mira with part of diaphragm values and update article with them and their analysis; but even now there is ability to say, that it ‘ll blur sides on them all down to f/11, and further sharpness is reduced by diffraction, so it’ll not has sharp frame sides.
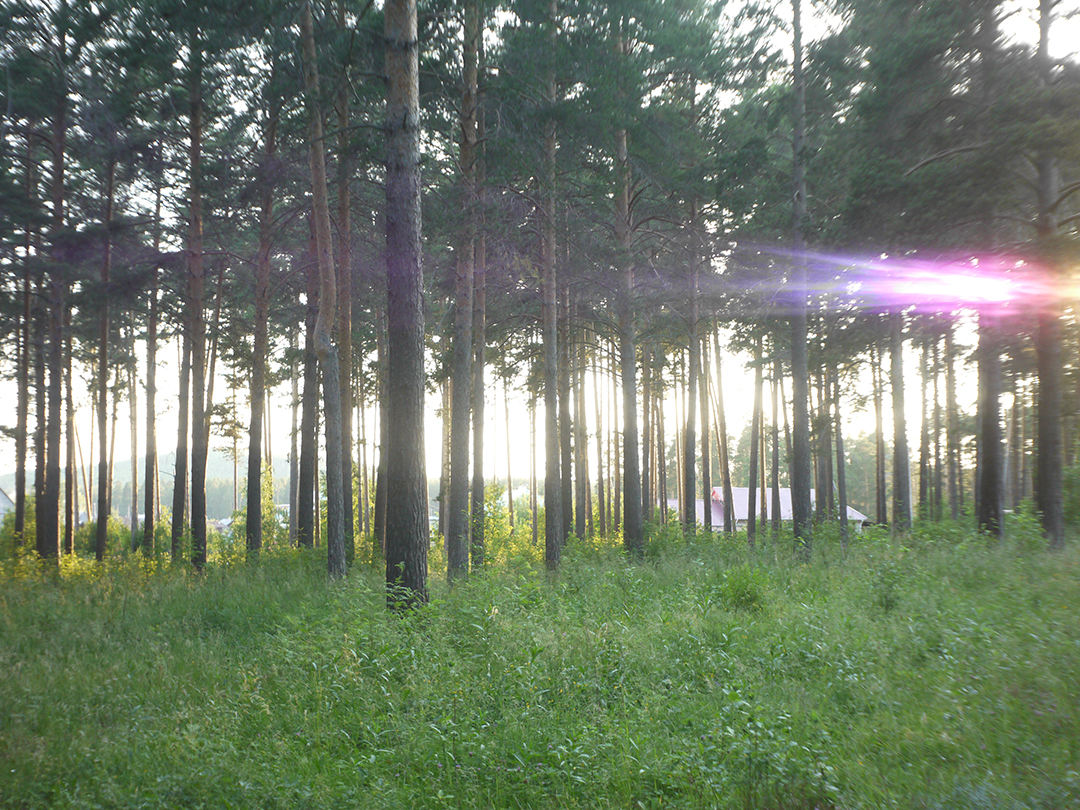

Photos in full resolution, made with Industar 69 can be seen on this page : Industar 69 lens test photos. Video with frontal and side lighting without YouTube recompression can be seen here : Industar 69 lens test videos.



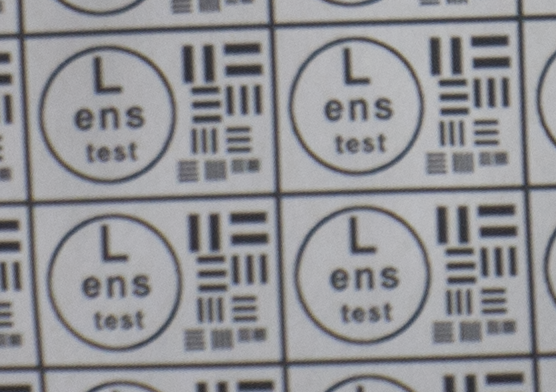
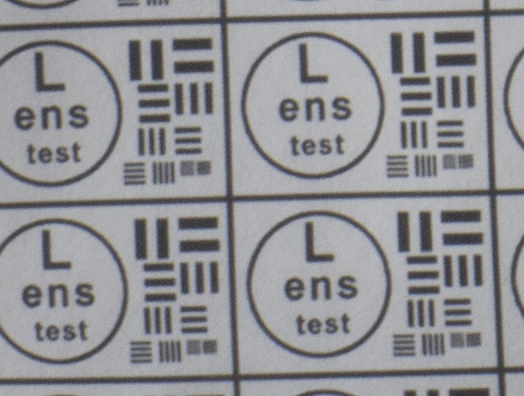
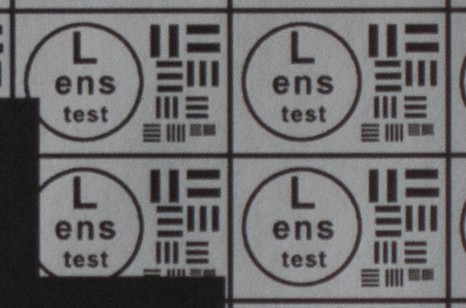
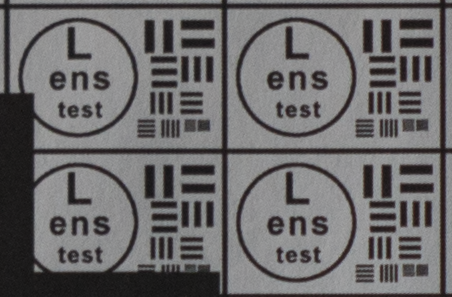
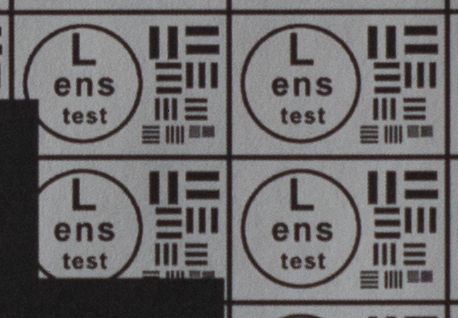
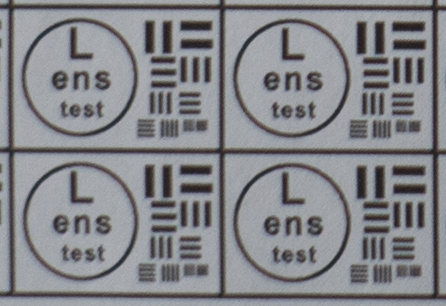
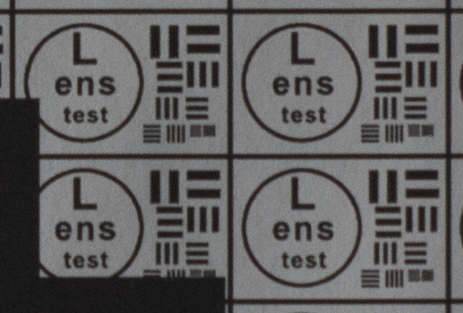
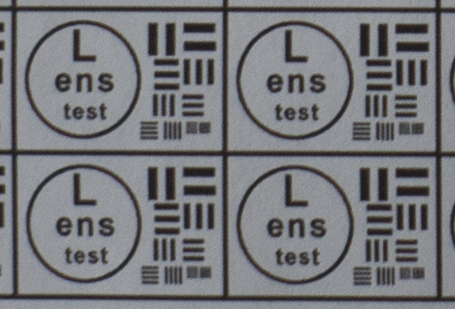
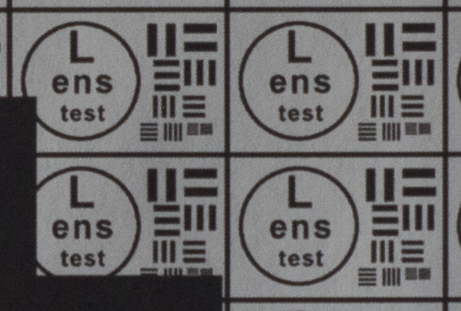
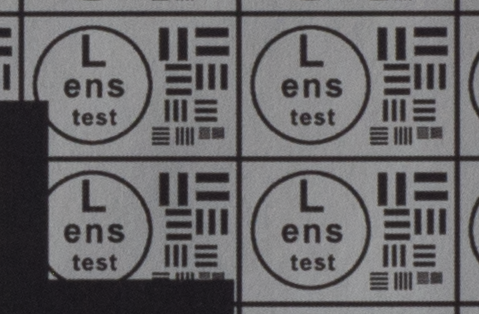
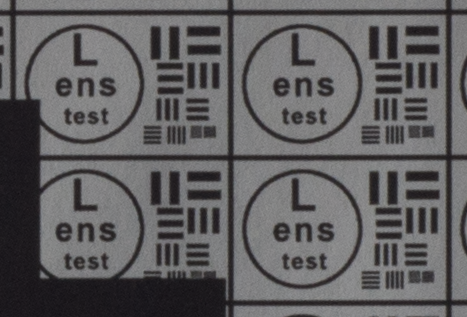
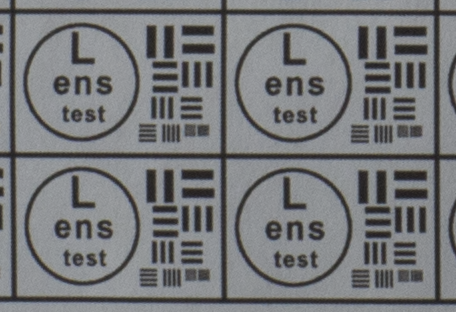
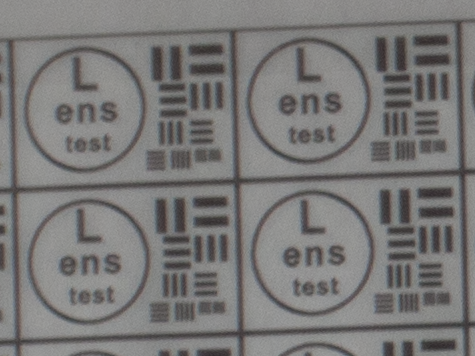
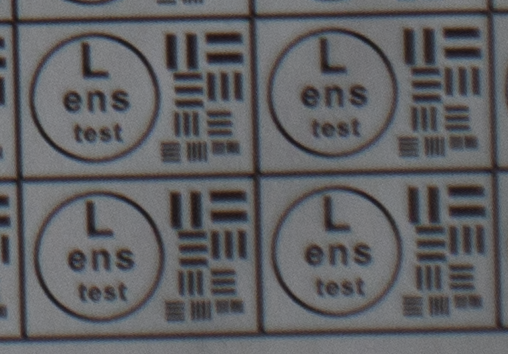
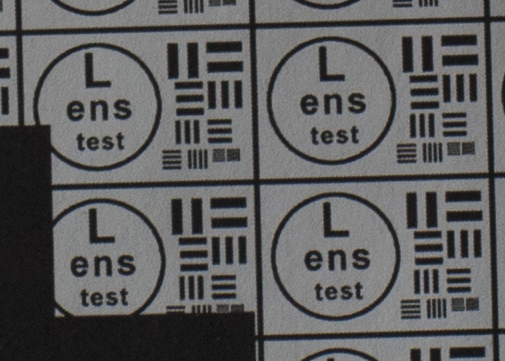
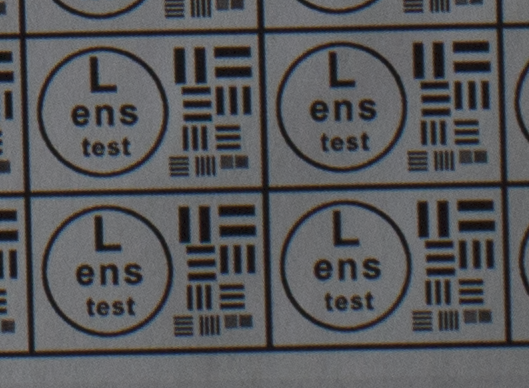
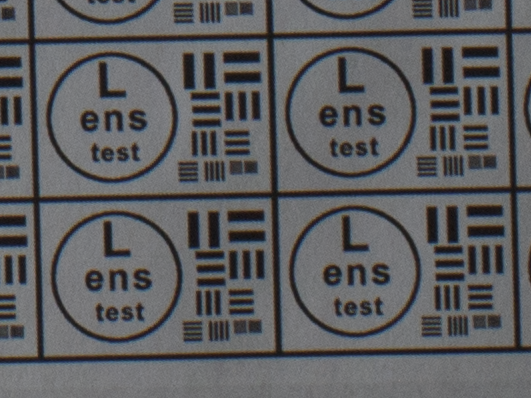
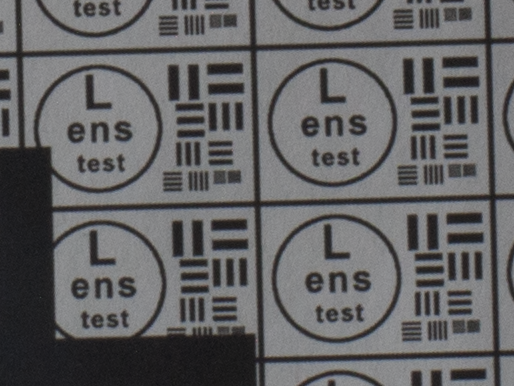
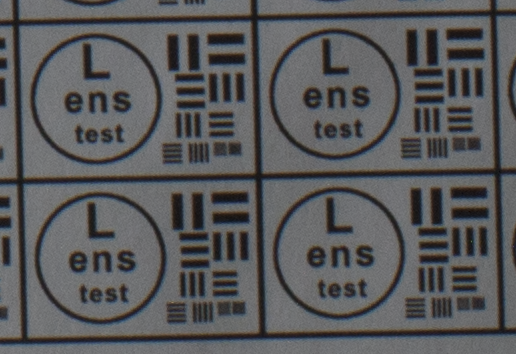
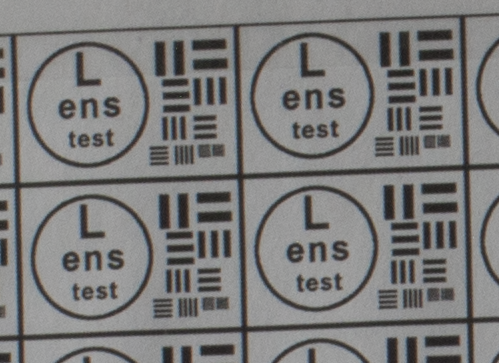
Test mira photos with Industar 69 lens ( 16.7.23 )
Made test mira photos with Industar 69 lens, as it was anticipated, on diaphragm 2.8 it blurs sides and center is very soft too, so it can be used only in some cases. With diaphragm 4 center is relatively sharp, sides are blurred approximately the same way. With 5.6 center is very sharp and sides are slightly better. On diaphragms 8 – 11 sides are more or less sharp, but on 11 diffraction starts to affect image, so maximal sharpness of Industar 69 can be achieved with diaphragms between 8 and 11. On 16 ( probably, this is a smaller diaphragm, because with closing down to limit mark goes far beyond 16 scale point and lighting sensor shows much larger its reduction, than on the other steps of diaphragm settings ) sides are sharp approximately the same way, as center, but whole image is blurred quite strongly with diffraction; so, it can be used only for narrow range of tasks.

All in all by photos of test mira there is ability to prove, that Industar 69 is more oriented on portrait, objects and macro shootings, as well as making photos of small groups of people in the center of frame, where sharpness of edges is not very important. More or less sharpness of edges on Micro 4/3 sensor can be achieved with it, but it is hardly applicable to making photos of landscapes, architecture and large groups of people in whole FOV. Lens is good enough with its own features, which should be accounted in work with it. Next I’ll test Vega 11U – one of the most sharp Soviet lenses with optical resolution 70/40 lines on mm ( center/edges ).